Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is a result of chronic liver disease. The liver tissue is replaced by fibrosis or scar tissue and this leads to a loss of liver 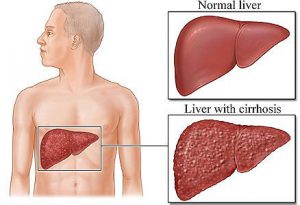 function. A person suffering from cirrhosis typically feels weak and tired. Some pain, nausea, and vomiting may be associated with the condition. Most of the time, cirrhosis is caused by alcoholism, hepatitis B or C, and fatty liver disease. Generally, cirrhosis is irreversible. Cirrhosis treatment focuses on preventing the disease from getting worse.
function. A person suffering from cirrhosis typically feels weak and tired. Some pain, nausea, and vomiting may be associated with the condition. Most of the time, cirrhosis is caused by alcoholism, hepatitis B or C, and fatty liver disease. Generally, cirrhosis is irreversible. Cirrhosis treatment focuses on preventing the disease from getting worse.
In advanced stages of cirrhosis the only option is a liver transplant. MELD stands for Model for End-Stage Liver Disease. MELD scores are used to set priorities for liver transplants.
In interpreting the MELD Score in hospitalized patients, the 3 month mortality rate is:
| MELD Score | Mortality Rate |
| 40 or more | 71.3% |
| 30-39 | 52.6% |
| 20-29 | 19.6% |
| 10-19 | 6.0% |
| Less than 9 | 1.9% |
As can be seen, if you have Hepatitis C, you need to know your MELD score. You can calculate your MELD score by using the Chronic Liver Disease Calculator.
Important Laboratory Values:
- Serum creatinine level in mg/dL
- Total bilrubin level in mg/dL
- International normalized ratio
Laboratory reports are very important, particularly reports of serum bilirubin. Reports of liver biopsies need to be presented if they exist. The bottom line is that the Social Security Administration will need to know the severity of the cirrhosis.
Note On Alcoholism: Most claimants suffering from cirrhosis are alcoholics. While the alcoholism may not be considered a disabling impairment, the liver disease may be considered disabling, if it cannot be reversed by stopping drinking. These cases can be difficult to present to the Social Security Administration.
What Our Clients Say:
Member:

Attorney Gregory Kornegay
Greg is a trial attorney in Wilmington with over 30 years of experience. Greg was born and raised in southeastern North Carolina. Before law school he managed a store with employees making a payroll every week. His first job out of law school was as an Assistant District Attorney investigating and trying cases for the State of North Carolina. Through the years he has handled many different types of cases – including death penalty cases.
Being married with children has been a blessing and a challenge, but has served him well in understanding the problems individuals and families face as they live out their lives. Greg believes that each case is different and the needs of each client are unique, but there are certain themes of life that we all share.


