Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy refers to a disease of the heart muscle. Symptoms include shortness of breath, fatigue, swelling in the 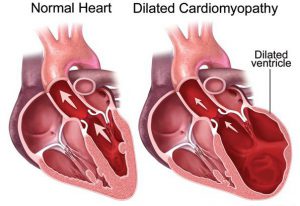 ankles, fluid in the lungs, heart enlargement, swelling of the liver, heart arrhythmias, passing out, angina, and palpitations. There are two main tests that will show the extent of heart muscle damage. A cardiac catheterization or an echocardiogram will show the left ventricular ejection fraction, which is the proportion of the blood and the ventricles which is ejected during a heartbeat.
ankles, fluid in the lungs, heart enlargement, swelling of the liver, heart arrhythmias, passing out, angina, and palpitations. There are two main tests that will show the extent of heart muscle damage. A cardiac catheterization or an echocardiogram will show the left ventricular ejection fraction, which is the proportion of the blood and the ventricles which is ejected during a heartbeat.
The Social Security Administration pays very close attention to the ejection fraction numbers:
| 65% ejection fraction | Normal |
| 30% or less | Person will feel extremely weak |
| 20% or less | Person will need heart transplant |
Any number approaching the 30% level should be very persuasive to the Social Security Administration for an award of benefits. However sometimes if alcoholism and/or drug abuse have caused cardiomyopathy, the Social Security judge may resist looking favorably upon the case because of an internal bias.
What Our Clients Say:
Member:

Attorney Gregory Kornegay
Greg is a trial attorney in Wilmington with over 30 years of experience. Greg was born and raised in southeastern North Carolina. Before law school he managed a store with employees making a payroll every week. His first job out of law school was as an Assistant District Attorney investigating and trying cases for the State of North Carolina. Through the years he has handled many different types of cases – including death penalty cases.
Being married with children has been a blessing and a challenge, but has served him well in understanding the problems individuals and families face as they live out their lives. Greg believes that each case is different and the needs of each client are unique, but there are certain themes of life that we all share.


